The software development landscape is rapidly evolving. New technologies and approaches are enabling businesses to build applications faster, more securely, and at lower costs than ever before.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the top software development trends that are impacting industries in 2025 and beyond. For each trend, we’ll look at real-world examples, data and statistics, as well as the implications for businesses.
10 Software Development Trends Across Industries in 2025 To Look For
1. Acceleration of Low-Code and No-Code Development
Low-code and no-code development platforms are simplifying software creation so that people with little to no coding skills can build apps. Instead of writing thousands of lines of complex code, developers can use visual, drag-and-drop interfaces.
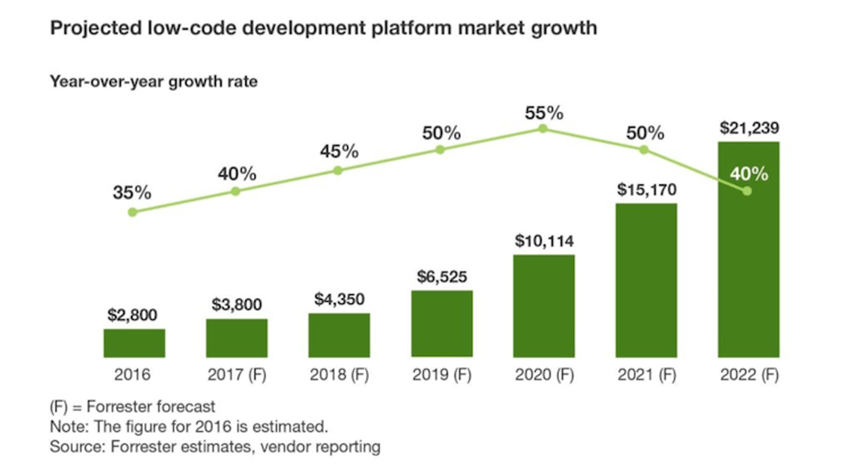
The pandemic accelerated adoption of these platforms. Per KPMG, 100% of enterprises using low-code have seen a positive ROI. The number of executives listing low-code as a top investment priority has nearly tripled since COVID-19 began.
Industry Impact
- Faster application development
- Empowering non-technical staff to build customized tools
- Freeing up developers to work on complex projects
- Enabling businesses to respond quicker to changing market conditions
Examples
Airtable – Collaborative database & no code platform used by Netflix, Nike, Amazon
Appian – Low code application development platform used by JP Morgan, UPS, Prudential
Bubble – No code web app builder used to develop web apps, SaaS products, marketplaces
2. Expanding Use of Cloud Computing
The pandemic forced a rapid shift to remote work and spotlighted the adaptability and cost efficiency of cloud computing. Businesses can scale computing resources up or down on demand. The cloud market grew by 6% in 2020 and is expected to double over the next few years.
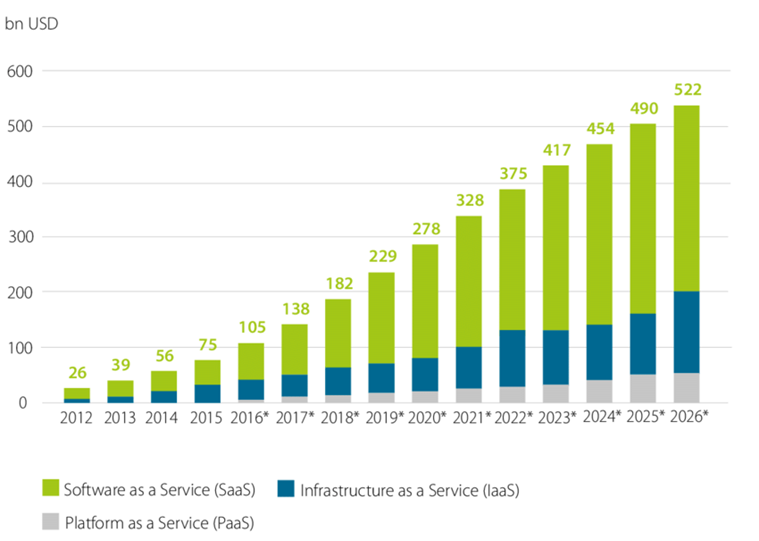
As this chart shows, the three largest cloud providers are all seeing strong double-digit revenue growth annually. To meet accelerating cloud demand, tech giants like Amazon and Accenture are aggressively expanding their cloud consulting teams.
Industry Impact
- Enabling remote work through cloud-based apps and storage
- Improving business agility and ability to scale computing needs
- Reducing upfront infrastructure costs by shifting to OPEX model
- Allowing businesses to focus less on managing datacenters
Examples
AWS – Over 200 cloud services including computing, storage, databases, analytics
Microsoft Azure – Cloud platform providing IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and AI capabilities
Google Cloud Platform – Suite of cloud computing services including computing, big data, ML
3. Emergence of Malicious Software Capabilities
As digital connectivity grows, so do vulnerabilities and opportunities for cyber attacks. Damaging ransomware attacks are expected to intensify, featuring tactics like double extortion – stealing data then demanding additional payment for its return.
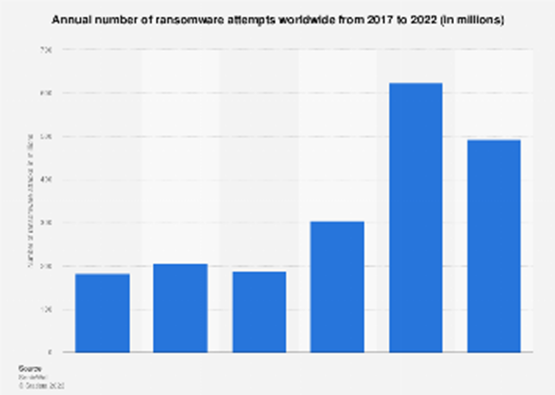
As shown above, the number of annual ransomware attacks has skyrocketed nearly 600% from 2015 to 2022. Payment demands have increased as well, with the average ransom up 31% from Q2 2020 to Q4 2020.
Industry Impact
- Surging demand for cybersecurity tools and personnel
- Businesses purchasing cyber insurance policies to mitigate risk
- Emergence of new regulations around cybersecurity practices
- Software innovations to prevent attacks and protect data
Examples
- Deep Instinct – Using deep learning to detect ransomware 0.3 seconds after activation
- Cybereason – Endpoint detection and response platform to prevent ransomware
- SentinelOne – AI-powered cybersecurity for real-time attack prevention
4. Expanding Implementation of AI Capabilities
Artificial intelligence adoption is accelerating across industries, enabling breakthroughs in efficiency, personalization, and new product capabilities.
The global AI market is forecasted to grow from $93.5 billion in 2021 to over $300 billion by 2024. Healthcare, banking, insurance, and manufacturing are seeing strong AI adoption growth.
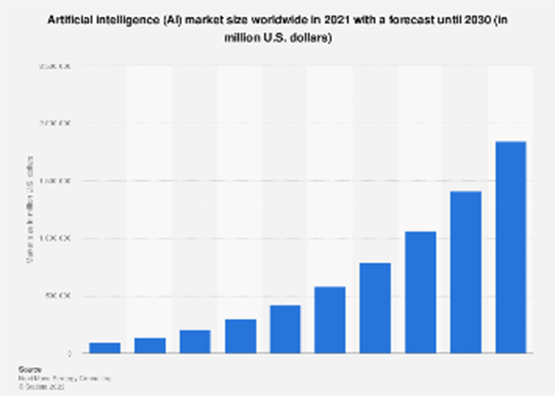
As this chart shows, AI adoption growth is led by the financial services sector. AI is allowing banks to provide hyper-personalized recommendations while reducing costs through process automation.
Industry Impact
- Automating business processes through robotic process automation (RPA)
- Utilizing machine learning for enhanced data analytics and insights
- Building chatbots and virtual assistants to improve customer experience
- Leveraging computer vision and predictive capabilities
Examples
nViso – Emotion detection APIs for contextual marketing campaigns
LemonBox – Using computer vision for quality assurance in manufacturing
Affectiva – Emotion AI for media testing, automotive safety, healthcare
John Deere – AI and computer vision for predictive maintenance on equipment
5. The Rise of Rust Programming Language
Rust is a systems programming language focused on speed, security, and memory safety. After being voted the most beloved language for four straight years, Rust is gaining strong momentum among developers.
As seen in Rust’s Tiobe index ranking, the language has moved up 26 spots in popularity since 2017. Rust is being adopted by tech giants like Microsoft, Amazon, Google, and Facebook for its performance and ability to prevent security vulnerabilities.
Industry Impact
- Preventing entire classes of memory safety bugs
- Building high-performance, scalable back end systems
- Enabling fearless concurrency without data races
- Developing mission-critical software with confidence
Examples
Cloudflare – Uses Rust for performance-critical networking infrastructure
Figma – Adopted Rust for the Figma plugin ecosystem
Microsoft – Added Rust support in Windows and Azure cloud development
6. Continuous Growth of IoT Connections
The Internet of Things (IoT) market continues to rapidly expand, as more devices and sensors connect to the internet. There is projected to be over 30 billion IoT connections by 2025, including wearables, appliances, vehicles, and manufacturing equipment.
As this forecast shows, the market is accelerating quickly, with IoT connections expected to nearly triple from 2018 to 2025. This connectivity boom enables real-time collection of data and remote monitoring capabilities.
Industry Impact
- Optimizing product design with usage data
- Enhancing supply chain visibility
- Preventative maintenance on equipment
- Workflow automation and smart offices
- Patient health monitoring and telemedicine
Examples
Peloton – Connected fitness equipment sends workout data to the cloud
Honeywell – Thermostats and smart home devices with remote access
John Deere – Sensors on tractors enable predictive maintenance
Bosch – Manufacturing sensors for process data and quality control
7. Progressive Web Apps Meet User Demand for App-Like Experiences
Progressive web apps (PWAs) bridge the gap between responsive sites and native mobile apps. PWAs load quickly, work offline, send push notifications, and can be installed to device home screens.
Starbucks has seen tremendous success with their PWA:
Other brands like Twitter, Uber, and Tinder have built PWAs to provide app-style speed and convenience without forcing users to download a native app.
Top industries, such as healthtech software development,have greatly leveraged the power of progressive apps.
Industry Impact
- Faster loading mobile web experiences
- Higher mobile conversion rates
- More engagement from app-resistant users
- Lower development/maintenance costs
- Streamlined customer journeys
Examples
- Starbucks – Mobile orders doubled after launch of PWA
- Lancôme – PWA increased conversion rate by 17%
- Trivago – PWA improved mobile bookings by 150%
- OLX – Cut load times from 12 secs to <3 secs with PWA
8. Shift to Microservices Architecture and Containerization
Monolithic applications can be challenging to update and scale. In contrast, a microservices model comprises independent modules that communicate via APIs. This approach streamlines development and deployment.
Developers praise microservices for their modularity, reusability across projects, and fault isolation capabilities. Paired with container technology like Docker, microservices enable one-click deployments to the cloud.
Industry Impact
- Faster feature development
- Improved application scalability
- Modernization of legacy applications
- Greater infrastructure flexibility
- Higher availability through redundancy
Examples
Netflix – Pioneered microservices approach, now deployed thousands of discrete services
PayPal – Migrated monolith to microservices for increased agility
Amazon – Leverages microservices architecture powering robust AWS ecosystem
Uber – Implements microservices using Node.js and React
9. Advancements in Blockchain-Based Software
Beyond powering cryptocurrencies, blockchain has appealing applications in software development – especially for applications dealing with transactions, contracts, or requiring tamper-proof data.
The global blockchain market is experiencing rapid growth at a CAGR of nearly 50%, according to ReportLinker forecasts. The transparency of sharing data across a decentralized, distributed network enables new functionality.
Industry Impact
- Smart contracts enabling automation without middlemen
- Supply chain optimizations through enhanced visibility
- Medical record interoperability and data integrity
- Digital rights management capabilities in media
Examples
SAP – Powers supply chain transparency through blockchain
Aetna – Blockchain solution for healthcare data exchange
Ascribe – Blockchain-based service for digital content attribution
Fox Media – Using blockchain for digital content rights and distribution
10. Mitigating the Software Developer Shortage with Outsourcing
As demand grows for software-powered innovation, businesses must keep up with explosive technology growth amidst a major tech talent shortage.
If this shortage goes unaddressed, 85 million jobs could go unfilled by 2030, representing $8.5 trillion in lost economic potential according to Korn Ferry. Increasingly, companies are turning to IT outsourcing to access specialized skills.
The IT outsourcing market is projected to grow steadily to $700+ billion by 2027. Partnerships and outsourcing provide access to global talent pools when hiring is difficult.
Industry Impact
- Tapping global talent pools amidst talent shortage
- Freeing up internal teams to focus on core competencies
- Improving ability to scale teams up and down
- Accessing niche technical and domain expertise
Examples
Apple/Infosys – 7 year strategic outsourcing deal
CSX Corporation/TCS – Outsourced 137 IT jobs to India-based TCS
OhioHealth/Accenture – Transferred 567 IT positions to Accenture
Conclusion
Software innovation is accelerating across every industry. As these examples illustrate, companies must adapt development strategies to keep up. By adopting modern architectures, automation, and testing integrations now, engineering teams can build faster and more securely.
Technologies like low-code platforms, microservices, and DevOps Services provide frameworks for increased output and reliability even amidst talent shortage headwinds. Meanwhile AI, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things open possibilities for data-driven intelligence and responsive, personalized customer experiences.
As software expands its reach deeper into products, services, and workflows, these development trends reflect techniques that allow its flexibility and future-proofing. Businesses investing in these emerging practices will improve resilience to both market forces and technological shifts over the horizon.


